
The Difference Between Off-Grid and On-Grid Solar Energy
2022-03-03 11:00When it comes to installing a solar power system, how to know what system is really you need? The on grid, off grid or the hybrid solar system? And because you’re investing in equipment that will last for many years, it is better for you to make the right choice.
If you partner with a reputable solar installer, they’ll be able to guide you through these decisions to get you the perfect system for your situation. However, doing a little homework on the front-end can’t hurt either.

What Is Off-Grid and On-Grid Solar Energy?
An off-grid solar energy system is not connected to the utility grid, whereas an on-grid (aka grid-tied) solar energy system is connected to the utility grid. Your choice of an off-grid system or on-grid system will determine:
1. Your access to electricity
2. What equipment is needed for excess production
3. What happens when the grid goes down
4. How you’re billed for electricity.
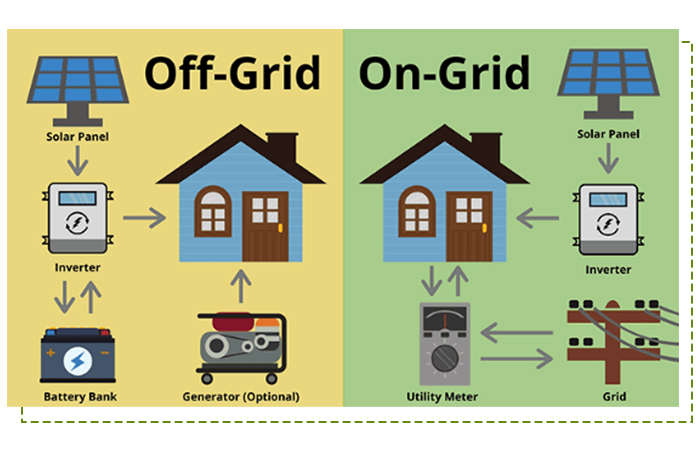
Difference #1: Your Access to Electricity
Electricity Access with Off-Grid Solar
What is meant by off-grid solar systems? With an off-grid solar system, you’re completely reliant on the sun and energy stored in batteries to power your home or business.
If you opt for a solar system that is not tied to the electric grid and you do not have a generator, you will only have electricity at two points:
1. When the sun is shining and your solar system is producing electricity.
2. When you’re pulling electricity previously generated by your solar system from a solar storage device, like batteries.
If you do not have batteries or a means to store your energy, you will have less or no electricity when it’s cloudy, and you will not have electricity at night.
With an off-grid system, you will not have access to extra electricity if you need it. What you are producing and what you have stored is all that’s there to power your equipment.
Electricity Access with On-Grid Solar
If you decide to install an on-grid solar system, you will always have access to electricity (unless the grid goes down), whether or not your solar system is producing or if you have batteries.
If your system is not producing any electricity or not producing enough electricity to power the devices, lights, machines, etc. that you’re using, you can pull energy from the utility grid to supplement it. This ensures you always have enough electricity for what you need.
Difference #2: What Happens to Excess Production

Excess Production with Off-Grid Solar
Most off-grid solar systems are designed to produce a certain amount of “extra” electricity in the daytime, which is sent to batteries for storage. The energy stored in those batteries can then be accessed when the system is not producing, like at night or during cloudy weather.
Depending on your energy goals, systems can be sized to produce enough excess electricity in the daytime to cover your entire energy usage around-the-clock.
Excess Production with On-Grid Solar
Depending on the time of day you use electricity, your solar system can produce excess energy. Instead of sending it to batteries as you would in an off-grid system, you can send it to the grid and you will be compensated for that electricity.
Grid-connected solar power has a distinct advantage over off-grid systems because net metering on other compensation methods from utility’s offer what is essentially free storage.
Difference #3: What Happens When the Grid Goes Down
Power Outages with Off-Grid Systems
Your solar system is working independently from the power grid. If there’s a bad storm or event that knocks out the power, your solar system can continue operating. You won’t notice changes in your service or access to electricity.
Power Outages with Grid-Tied Systems
By connecting to the grid, you get access to electricity whenever you need it. However, you’re also subject to some rules.
While this is a disadvantage of grid-tied systems over off-grid systems, if keeping things up-and-running during a power outage is important to you, then you may be interested in adding batteries to your grid-tied system.
Difference #4: How You’re Billed for Electricity

Electricity Bills with an Off-Grid System
If your PV system is not tied to a grid, you won’t receive an electric bill at all. However, even with no electric bill, off-grid systems are often more expensive because of the additional equipment like batteries that are needed to make it viable.
Electricity Bills with a Grid-Tied System
If you opt for a grid-tied system, you could still see a few minimal charges on your electricity bill, even if your solar system provides 100% of your electricity.
One type of charge you may continue to see is the service fee or delivery charge. This is the cost levied on customers for connecting their home or business to the grid. For many utilities, this fee is a flat rate that is not impacted by how much electricity you use.
Another type of charge you can see is demand charges. Demand charges are typically levied on commercial properties and are the increased electric rate you pay for the power you use during a peak demand period. The peak demand period is typically the 15-minute period in which your business uses the most electricity.
